Hugging Face introduces a benchmark for evaluating generative AI in healthcare tasks
There's a growing interest in using generative AI models in healthcare, believed by some to potentially boost efficiency and uncover new insights. Yet, concerns arise about their flaws and biases possibly leading to negative health outcomes. A critical question remains: How can we accurately assess the usefulness or risks these models pose, especially in tasks like summarizing patient records or providing health-related answers?
To address this, the AI startup Hugging Face, in collaboration with Open Life Science AI and the University of Edinburgh's Natural Language Processing Group, introduced Open Medical-LLM. This new benchmark test aims to evaluate generative AI models' performance on various medical tasks systematically. By integrating tests from existing datasets, Open Medical-LLM assesses models on a wide array of medical knowledge, including anatomy and clinical practice, by utilizing material from U.S. and Indian medical exams, among other sources.
Hugging Face describes Open Medical-LLM as a tool for identifying strengths and shortcomings of AI approaches in healthcare, hoping it will foster advancements and improve patient care. However, there's caution from the medical community about overreliance on such benchmarks. Critics argue they might not accurately reflect models' applicability in real-world medical settings.
Instances like Google's AI for detecting diabetic retinopathy in Thailand highlight the challenges of applying AI in healthcare. Despite showing promise in lab settings, the tool struggled in actual clinical environments, leading to frustration among healthcare providers and patients.
Despite these hurdles and the absence of generative AI tools among FDA-approved AI medical devices, benchmarks like Open Medical-LLM play a critical role. They remind us of the current limitations of AI in healthcare and the necessity for thorough, real-world testing. Open Medical-LLM is not the final answer but a step toward better understanding and eventually integrating AI into healthcare more effectively.
 Why Meta is looking to the fediverse as the future for social media
Why Meta is looking to the fediverse as the future for social media Microsoft’s Surface and Xbox hardware revenues take a big hit in Q3
Microsoft’s Surface and Xbox hardware revenues take a big hit in Q3 Augment, a competitor of GitHub Copilot and backed by Eric Schmidt, emerges from stealth mode with a launch of $252 million
Augment, a competitor of GitHub Copilot and backed by Eric Schmidt, emerges from stealth mode with a launch of $252 million IBM advances further into hybrid cloud management with its $6.4 billion acquisition of HashiCorp
IBM advances further into hybrid cloud management with its $6.4 billion acquisition of HashiCorp Perplexity is raising over $250 million at a valuation of between $2.5 billion and $3 billion for its AI search platform, according to sources.
Perplexity is raising over $250 million at a valuation of between $2.5 billion and $3 billion for its AI search platform, according to sources. Apple announces May 7 event for new iPads
Apple announces May 7 event for new iPads Gurman: iOS 18 AI features to be powered by entirely On-Device LLM, offering privacy and speed benefits
Gurman: iOS 18 AI features to be powered by entirely On-Device LLM, offering privacy and speed benefits Meta aims to become the Microsoft of headsets
Meta aims to become the Microsoft of headsets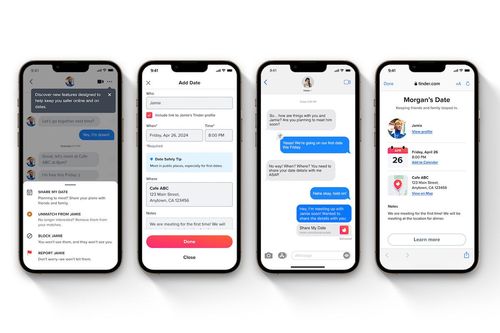 Tinder introduces a 'Share My Date' feature allowing users to share their date plans with interested friends
Tinder introduces a 'Share My Date' feature allowing users to share their date plans with interested friends This is Tesla's effective solution for the recalled Cybertruck accelerator pedals
This is Tesla's effective solution for the recalled Cybertruck accelerator pedals
